Solar Power Industry in India: Growth, Challenges, and the Road Ahead
Introduction
India, endowed with over 300 sunny days annually and expansive arid and semi-arid regions, holds immense potential for solar energy generation. In the past decade, the country has rapidly expanded its solar capacity, moving from less than 10 GW in 2015 to over 108 GW by April 2025. This growth has been propelled by declining costs, favourable government policies, a growing investor base, and a national commitment to sustainability. This comprehensive article explores the current status of India’s solar power sector, its investment landscape, domestic and global competition, technology trends, manufacturing ecosystem, and future outlook.
1. Present Status of the Solar Power Industry in India
Installed Capacity and Generation
As of April 2025:
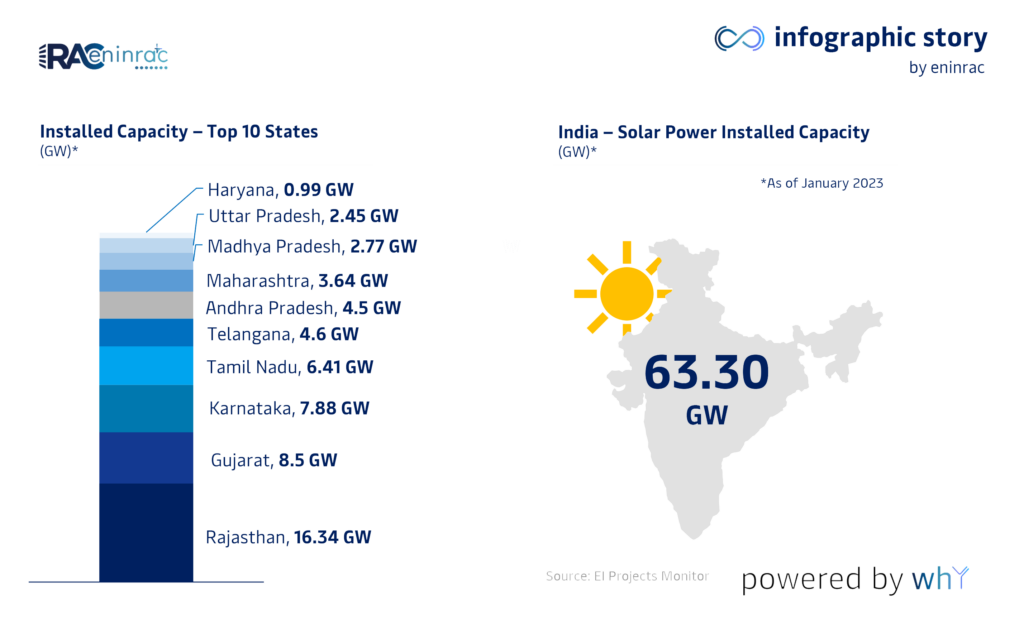
- Installed Solar Capacity: 108 GW (AC)
- Annual Generation: 144 TWh
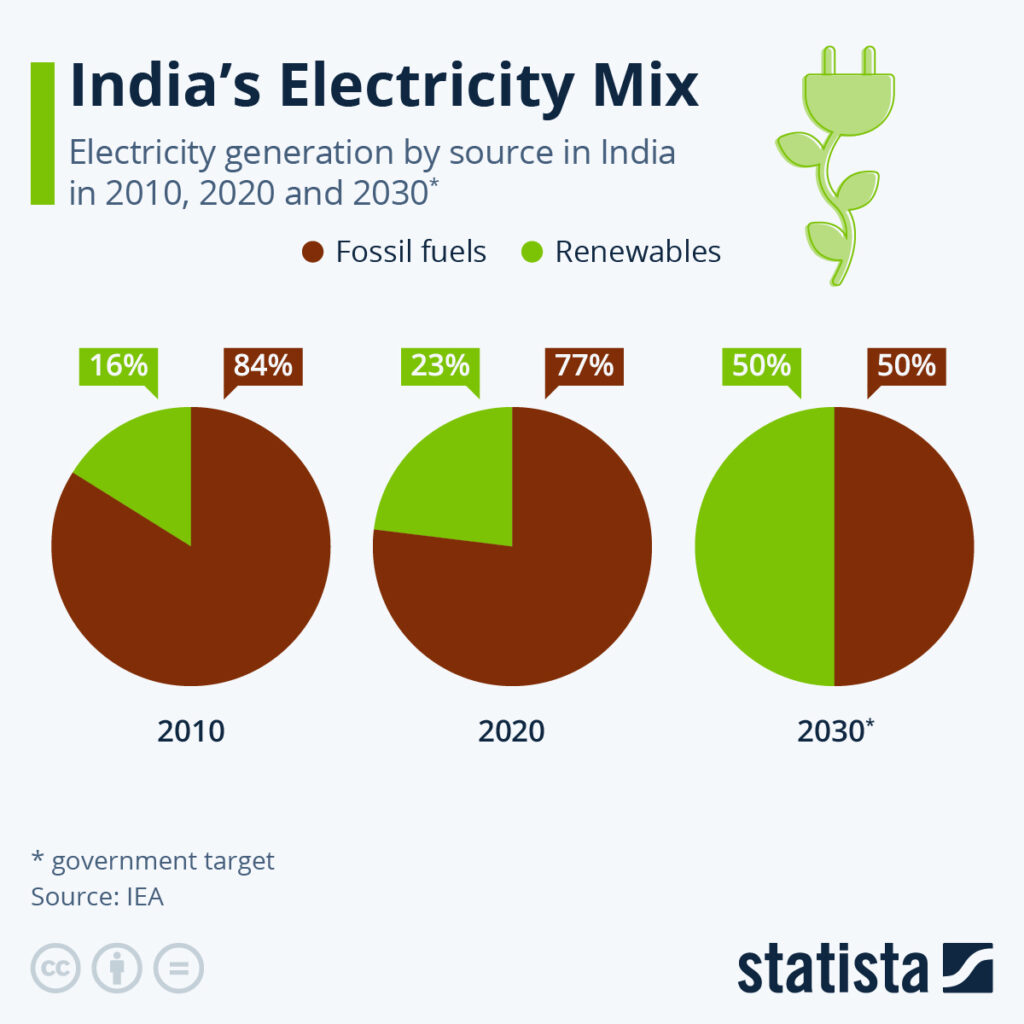
- Solar power now contributes around 18% of India’s total electricity generation capacity, positioning India as the fifth-largest solar market globally.
Investment and Financials
- Investment (FY 2022–2024): Over ₹1.5 lakh crore (~$18 billion)
- Industry Turnover (FY 2024–25): Estimated ₹2.25–2.5 lakh crore
Costs and ROI
- Utility-scale Cost: ₹2.5–₹3.5/kWh
- Rooftop System Cost: ₹45,000–55,000/kW
- 1 MW Plant Cost: ₹4–5 crore
- Typical ROI: 11% to 17% IRR, with a payback period of 6–9 years for utility-scale projects
2. Investment Plans, Growth Trends, and Financing Challenges
Growth Outlook
India aims to add 30–40 GW of solar capacity annually to achieve 280–300 GW by 2030.
Major Investors
- Adani Green Energy: Targeting 45 GW by 2030
- Reliance New Energy Solar: ₹75,000 crore investment in a Giga solar complex
- Tata Power Solar, ReNew Power, Azure Power, and NTPC Green Energy are active players
Financing Mechanisms
- Public-Private Partnerships (PPP)
- Green Bonds (e.g., Avaada’s ₹1,440 crore issue)
- Multilateral loans (e.g., ADB, World Bank)
Key Challenges
- Delays in PLI disbursements
- Land acquisition hurdles
- High capital cost for small developers
3. Technology & Domestic Manufacturing Ecosystem
Technology Status
- Dominant: Mono-PERC
- Emerging: N-type TOPCon, HJT, Bifacial modules, G12 format
Manufacturing Capacity (2025)
- Modules: 63 GW/year
- Cells: 25 GW/year
- Wafer/Polysilicon: <5 GW (still heavily imported)
Notable Manufacturers
- Waaree: 13.3 GW modules, 5.4 GW cells
- Emmvee: 6.6 GW modules, 2.5 GW cells
- INA Solar: 4 GW modules (to 8 GW by 2027)
- Vikram Solar: 4.5 GW modules; HJT in development
- Avaada Electro: 7 GW target by 2025
Key Inputs & Constraints
- High dependency on imported polysilicon, wafers
- Price volatility in input materials
- Skill shortages in solar manufacturing workforce
4. Competition and Strategic Response
Global Competition
- Chinese Dominance: 80%+ global solar manufacturing
- Lower Costs: Chinese modules priced at $0.17–0.22/W vs India’s $0.24–0.28/W
Strategic Indian Responses
- Vertical Integration: Adani, Reliance
- PLI Scheme: ₹24,000 crore to support manufacturing
- ALMM List: Domestic preference in public projects
- Quality Assurance: PVEL, BIS, IEC certification emphasis
5. EPC Contractors and Major Players
Key Indian Players
| Company | Module Cap. | Cell Cap. | Notes |
| Waaree | 13.3 GW | 5.4 GW | Leading exporter |
| Emmvee | 6.6 GW | 2.5 GW | Supplies NTPC, Europe |
| INA Solar | 4 GW (2025) | Planned | Aggressive expansion |
| Vikram Solar | 4.5 GW | 3 GW | HJT modules, Tier-1 supplier |
| Avaada Electro | 7 GW (2025) | Planned | TOPCon G12 modules |
EPC Firms
- Tata Power Solar, Sterling & Wilson, Mahindra Susten, Jakson Group
6. Module Availability and Pricing
| Module Type | Indian Price (₹/W) | Import Price (₹/W) |
| Mono-PERC | 22–25 | 17–19 |
| TOPCon | 26–28 | 21–23 |
| Bifacial Glass | 27–30 | 22–24 |
Advanced Indian modules are closing the gap in efficiency and reliability with global products.
7. Government Support Mechanisms
- PLI Scheme: ₹24,000 crore for module/cell/wafer/polysilicon manufacturing
- ALMM Mandate: Domestic-only for government projects from 2026
- Customs Duties: 40% (modules), 25% (cells) on imports
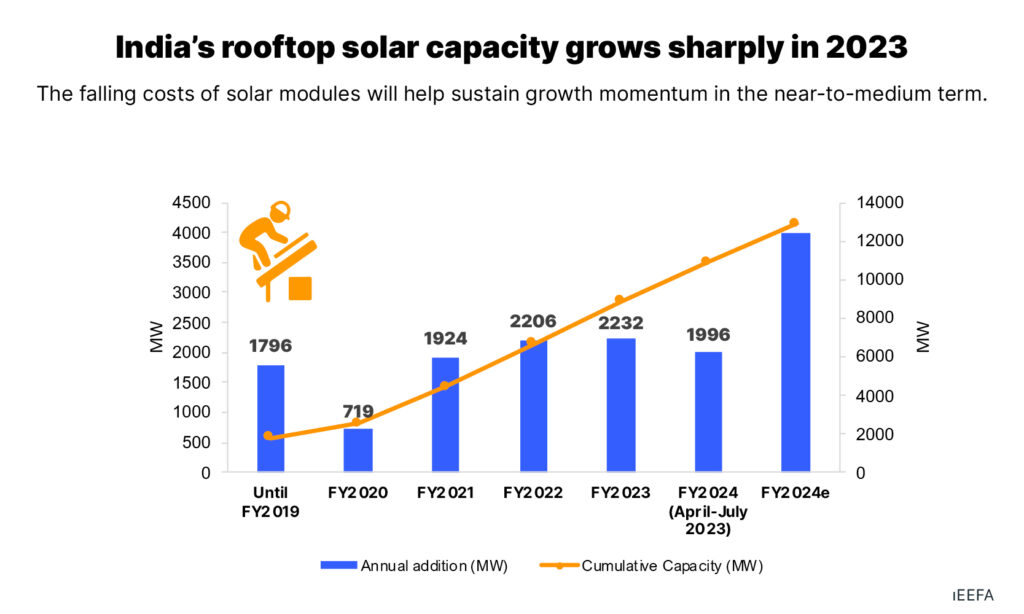
- PM Surya Ghar Yojana: ₹75,000 crore rooftop subsidy scheme
- Open Access Rules (2022): Easier access for C&I consumers to green power
8. Case Studies
A. Bhadla Solar Park, Rajasthan
- Capacity: 2,245 MW
- Investment: ₹~17,500 crore
- Tariff: Record low ₹2.44/kWh
- Challenges: Water scarcity, e-waste, social impacts
B. Avaada Electro, Maharashtra
- Capacity: 7 GW target
- Module Type: G12 TOPCon
- Financing: Green bonds, state incentives
- ALMM-Approved: Eligible for government tenders
C. Kamuthi Solar, Tamil Nadu
- Capacity: 648 MW
- Execution: 8 months by Adani Green
- Innovation: Robotic cleaning
- Yield: ~1.35 TWh/year
D. Floating Solar at Omkareshwar, MP
- Capacity: 600 MW planned
- Tariff: ₹3.20–3.26/kWh
- Challenges: Anchoring in storm-prone zones
- Developer: RUMSL, SJVN, NHDC, AMP Energy

9. Manufacturer Tech Performance Comparison
| Manufacturer | Tech | Power (Wp) | Efficiency | Degradation | Warranty |
| Vikram Solar | HJT, PERC | 600–700 | 21.2–22.5% | 0.55–0.7% | 25 yrs, ≥80.2% retained |
| Emmvee | TOPCon, HJT | Up to 720 | 21.5–23% | 0.5% | 25 yrs, ≥80% retained |
| Avaada | TOPCon G12 | 720 | 22.5–23% | 0.45–0.5% | 25 yrs, ≥80.2% retained |
| INA Solar | TOPCon G12 | 715–720 | 22.0–23% | 0.5% | 25 yrs, ≥80.5% retained |
| JinkoSolar | N-type | 715–730 | 22.5–23.2% | 0.4–0.6% | 25–30 yrs, ≥80–82% retained |
10. Company Focus: IB Solar
- Entity: Integrated Batteries India Pvt. Ltd. (IB Solar)
- Capacity: 700 MW modules (targeting 5 GW by 2027)
- Tech: Mono-PERC and emerging TOPCon
- Reach: North India (Delhi NCR, UP, MP, Jharkhand)
- Specialization: Integrated solar + storage solutions
- Certification: ALMM approved
References
- MNRE
- IEA Solar PV Supply Chain Report
- Wikipedia – Solar Power in India
- Mercom India
- Energy Tracker Asia
- PV-Tech
- Times of India
- Rewa Ultra Mega Solar Limited (RUMSL)
- IEEFA Reports
- CENFA India
- Global Solar Council
- Asian Development Bank
- World Bank India
- IB Solar
- Nature.com
- Cipher News
- SolarQuarter
- PIB India
Conclusion
India has established itself as a global leader in solar energy, leveraging abundant natural resources, supportive policies, and a vibrant entrepreneurial ecosystem. However, to sustain momentum, India must address challenges related to manufacturing integration, skill shortages, long-term financing, and resilience to climate risks. Floating solar, high-efficiency modules, storage coupling, and innovative business models will define the next phase. With timely reforms and strategic focus, India can not only meet its climate targets but also emerge as a global manufacturing and innovation hub for solar energy.

