The Role of Renewable Energy in Indian Railways’ Sustainability Goals
Introduction
Indian Railways, one of the world’s largest railway networks, is pivotal to India’s transportation infrastructure. Recognizing its significant energy consumption and environmental impact, Indian Railways has embarked on an ambitious journey to achieve net-zero carbon emissions by 2030. Central to this mission is the adoption of renewable energy sources—primarily solar and wind—and the implementation of energy-efficient practices across its operations.
1. Indian Railways’ Energy Consumption and Mix
As of 2023-24, Indian Railways consumed approximately 33,000 GWh of electricity for traction and other operations, marking a significant increase from 30,028 GWh in 2022-23 . The energy mix comprises both electricity and diesel, with a notable shift towards electrification. In 2023-24, diesel consumption was recorded at approximately 1.46 million tonnes, a decrease from previous years, indicating a move towards cleaner energy sources .
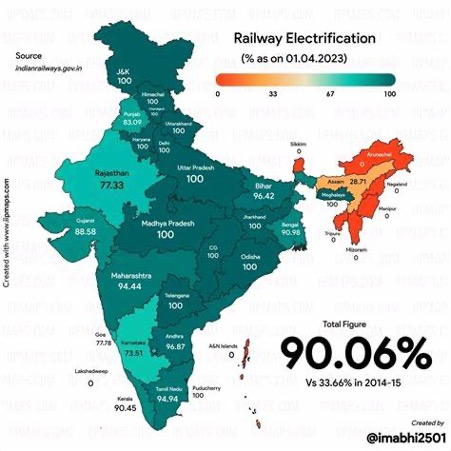
The electrification of the railway network has been a significant focus, with over 96% of the broad-gauge network electrified by April 2024 . This transition not only reduces greenhouse gas emissions but also enhances operational efficiency and reduces fuel costs.
2. Adoption of Renewable Energy: Solar and Wind Initiatives
Solar Energy Initiatives
- Rooftop Solar Installations: Indian Railways has made significant strides in harnessing solar energy. As of February 2025, it has installed 209 MW of solar power across 2,249 stations and service buildings. This expansion aligns with the government’s commitment to promoting renewable energy and environmental sustainability.
- Solar-Powered Trains: In a pioneering move, Indian Railways introduced trains equipped with rooftop solar panels. These panels power onboard services like lighting and fans, reducing diesel consumption. For instance, hybrid trains combining diesel and solar power have been launched, with each train saving approximately 21,000 liters of diesel annually.
- Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs): To further its renewable energy goals, Indian Railways signed a 170 MW power purchase agreement with the Madhya Pradesh government. This deal secures solar power at ₹2.15 per kWh, the lowest rate in India, and underscores the railway’s commitment to sustainable energy procurement.

Wind Energy Adoption
Complementing its solar initiatives, Indian Railways is also investing in wind energy. It has commissioned 103 MW of wind power plants, contributing to its renewable energy portfolio.
Additionally, innovative projects like installing wind turbines along railway tracks are being explored. These turbines harness the wind generated by passing trains, converting it into usable energy and showcasing Indian Railways’ commitment to innovative renewable solutions.

3. Planned Introduction of Hydrogen Engines in Railways
Indian Railways is exploring hydrogen fuel cell technology as a sustainable alternative to diesel-powered trains. The first hydrogen-powered train is expected to undergo trials on the Jind-Sonipat route in Haryana by June 2025 . This initiative is part of the ‘Hydrogen for Heritage’ program, aiming to deploy 35 hydrogen trains on heritage and mountainous routes.
The hydrogen train, developed by the Integral Coach Factory in Chennai, boasts a 1,200 horsepower engine, making it one of the most powerful hydrogen trains globally . These trains will utilize hydrogen fuel cells to generate electricity, emitting only water vapor, thus significantly reducing carbon emissions.

4. Global Perspectives: Lessons from Developed and Developing Countries
Germany
Germany has been a pioneer in hydrogen-powered trains, introducing the world’s first commercial hydrogen-powered passenger train in 2018. The Coradia iLint trains operate on a 62-mile line in Lower Saxony, producing zero direct emissions and offering a range of approximately 620 miles on a single fill .
Japan
Japan introduced its first hydrogen-powered train, the FV-E991 series, in 2022 on the Tsurumi Line between Yokohama and Kawasaki. This initiative reflects Japan’s commitment to sustainable transportation solutions .
United States
In California, the Zero-Emission Multiple Unit (ZEMU) hydrogen train began operations between Redlands and San Bernardino in 2024. This project aims to address air quality issues and aligns with California’s goal of carbon neutrality by 2045 .
Lessons for India
India can learn from these global initiatives by:
- Investing in Infrastructure: Developing hydrogen refueling stations and maintenance facilities is crucial for the successful deployment of hydrogen trains.
- Public-Private Partnerships: Collaborating with private entities can accelerate the adoption of new technologies and share the financial burden.
- Pilot Projects: Implementing pilot projects on select routes can help assess the feasibility and scalability of hydrogen-powered trains.
5. Energy-Efficient Practices
Electrification of Railway Lines
A cornerstone of Indian Railways’ sustainability strategy is the electrification of its network. As of 2024, approximately 63,500 route kilometers have been electrified, covering over 96% of the broad-gauge network .
This shift from diesel to electric traction not only reduces greenhouse gas emissions but also enhances operational efficiency and reduces fuel costs.
Introduction of Energy-Efficient Locomotives
Indian Railways is modernizing its fleet with energy-efficient locomotives. For instance, the recently inaugurated 9,000 HP electric locomotive at the Dahod workshop in Gujarat represents a significant technological advancement, aiming to bolster efficiency and strengthen the electric rail infrastructure.
Implementation of LED Lighting
To reduce energy consumption, Indian Railways has replaced conventional lighting with LED lights across stations, trains, and office buildings. This transition not only lowers electricity usage but also reduces maintenance costs and enhances illumination quality.
Regenerative Braking Systems
Regenerative braking technology is being adopted in trains to improve energy efficiency. This system captures the kinetic energy during braking and converts it into electrical energy, which can be reused or fed back into the power grid, thereby reducing overall energy consumption.
6 Indian Railways’ Energy Consumption and Mix
- Energy Consumption: In the fiscal year 2023-24, Indian Railways consumed approximately 33,000 GWh of electricity for traction and operations.
- Electrification Progress: As of January 2024, 94% of Indian Railways’ lines had been electrified, with a goal to achieve 100% electrification by mid-2024. REN21
- Energy Mix: Currently, 90% of Indian Railways’ trains utilize electrical power, with diesel accounting for the remaining 10%. The Times of India
7 Solar and Wind Energy Initiatives
- Solar Installations: By February 2025, Indian Railways had installed 2,249 solar power plants at railway stations and service buildings across the country. DD News
- Wind Energy Integration: Indian Railways has secured 3,427 MW of installed wind capacity, supplementing its 4,260 MW of installed solar power, to meet its growing traction energy needs. WindInsider+1Press Information Bureau+1
- Power Purchase Agreements: Indian Railways signed a 170 MW power purchase agreement with the Madhya Pradesh government, securing solar power at ₹2.15 per kWh, the lowest rate in India.
8 Hydrogen Train Development
- Hydrogen Train Trials: India’s first hydrogen-powered train is expected to undergo trials on the Jind-Sonipat route in Haryana by December 2024. India Today
- Hydrogen for Heritage Initiative: Under this initiative, Indian Railways plans to deploy 35 hydrogen trains on heritage and mountainous routes, with ₹600 crore earmarked for infrastructure development. Metrorail Today
- Hydrogen Train Engine: The hydrogen train, developed by the Integral Coach Factory in Chennai, boasts a 1,200 horsepower engine, making it one of the most powerful hydrogen trains globally.
9 Global Hydrogen Train Initiatives
- Germany: The Coradia iLint is the world’s first passenger train powered by a hydrogen fuel cell, operating in Germany since 2018. Society of Women Engineers+3WIRED+3Alstom+3
- Japan: The FV-E991 series, nicknamed HYBARI, is a hydrogen fuel cell electric multiple unit train operated by East Japan Railway Company (JR East) from 2022. jnsforum.com+3Wikipedia+3YouTube+3
- United States: In California, the Zero-Emission Multiple Unit (ZEMU) hydrogen train began operations between Redlands and San Bernardino in 2024.
10 Energy-Efficient Practices
- Electrification Milestone: Indian Railways has electrified 60,814 km of its broad-gauge network as of November 2023. Press Information Bureau
- LED Lighting: Indian Railways has replaced conventional lighting with LED lights across stations, trains, and office buildings to reduce energy consumption.
- Regenerative Braking Systems: Regenerative braking technology is being adopted in trains to improve energy efficiency by capturing kinetic energy during braking and converting it into electrical energy.
11 Conclusion
Indian Railways’ commitment to renewable energy and sustainability is evident through its extensive initiatives in solar and wind energy adoption, electrification, and energy-efficient practices. By aiming for net-zero carbon emissions by 2030, it not only contributes to India’s environmental goals but also paves the way for a greener and more sustainable future in rail transportation.
12 References
- Indian Railways: On Track to Net Zero
This United Nations report outlines Indian Railways’ strategies to achieve net-zero carbon emissions by 2030, focusing on renewable energy adoption and energy efficiency improvements. - Indian Green Railway by 2030 – Policies
The International Energy Agency discusses India’s plan to transform its railway system into a “green railway” by 2030, highlighting measures like electrification and renewable energy integration. - Indian Railways to Become Net Zero Carbon Emitter by 2030
A Press Information Bureau release detailing Indian Railways’ initiatives, including the commissioning of solar and wind power plants, to achieve net-zero carbon emissions. - Sustainability Track: Indian Railways Aims for Net Zero
An article from Power Line magazine discussing Indian Railways’ advancements in solar and wind energy, network electrification, and development of hydrogen-fuel trains. - Indian Railways Accelerates Towards Net-Zero With 10,000 MW Clean Energy Vision By 2030
SolarQuarter reports on Indian Railways’ commitment to achieving net-zero emissions by 2030 through extensive adoption of solar and wind energy. - Indian Railways Aims for Net Zero Carbon Emissions by 2030
An article from Economy Global highlighting Indian Railways’ commissioning of solar and wind energy plants as part of its net-zero carbon emissions goal. - Indian Railways Plans to Go Nuclear: Addressing 8.2 GW Energy Needs by 2030
An insight into Indian Railways’ consideration of nuclear power, specifically Small Modular Reactors, to meet its energy requirements for achieving net-zero emissions. - Indian Railways is Marching Towards Achieving the Objective of Net Zero Carbon Emission by 2030
A Press Information Bureau release discussing Indian Railways’ plans to meet its energy requirements through non-fossil sources, including solar, wind, and nuclear power. - How India Electrified 45% of Its Railway Network in Just Five Years
An article from Energy Monitor detailing the rapid electrification of Indian Railways and its impact on the country’s energy independence and environmental goals. - Sustainable Rail Infrastructure of Indian Railways
A research paper reviewing current practices, challenges, and potential pathways toward achieving sustainability in Indian Railways.
Excellent write up summarising the entire Renewable Energy transformation of the Indian Railways. It’s motivating to read the article which gives so much data as well as a story of progress
Thanks Ksudtubhsn